I get it — You are tired of searching for datasets online for your machine learning project or maybe for analyzing a popular twitter trend.
Today we will learn how to generate your own custom dataset from twitter by using hashtag search.
Want to skip the post and see the good stuff directly? Here is the Github repo for you
Understanding the twitter policies for robots
First things first, let's make sure we follow the policies made by twitter.com for robots to follow while crawling so that we don’t run into any legal issues. Let's go to https://twitter.com/robots.txt
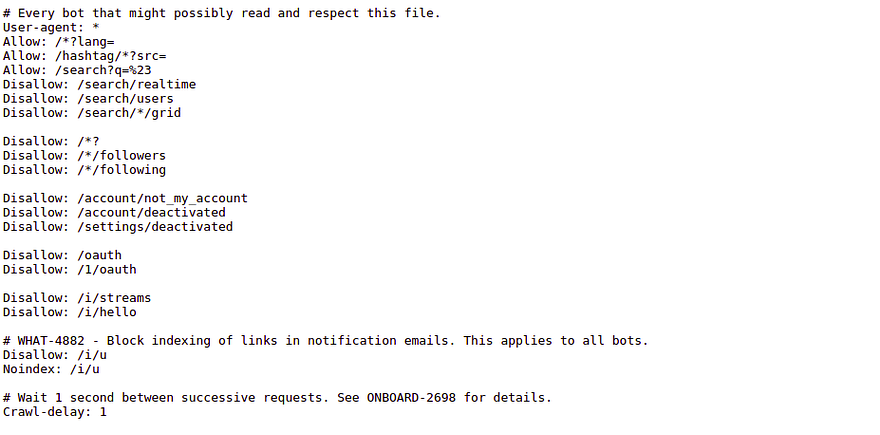
We can see twitter has allowed all the robots ( look at User-agent line ) to use the hashtag search (look at Allow: /hashtag… line) and requested to make a 1-second delay (look at Crawl-delay line) between the crawl requests.
User-agent: *
Allow: /hashtag/*?src=
Crawl-delay: 1
Walking through the code
This assumes that you have some basic knowledge of python and scrapy. If you are interested in only generating your own dataset, skip this section and go to sample crawl section directly or visit GitHub repo.
Gathering tweets URL by searching through hashtags
For searching for tweets we will be using the legacy twitter website. Let’s try searching for #cat https://mobile.twitter.com/hashtag/cats. This legacy version doesn't use javascript to load the data which makes our job super easy.
I choose a lazy person to do a hard job. Because a lazy person will find an easy way to do it.
― Bill Gates
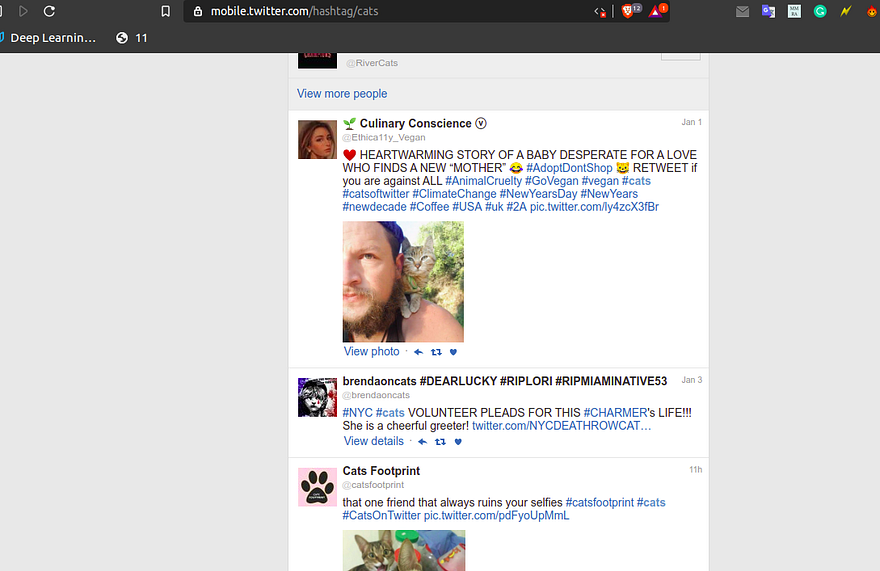
Finding all the tweet URL for our hashtag search — find_tweets( ) function
If you want to look at the complete code at once. Here’s Github repo.
Explanation: We will find the xpaths for all the tweets URL in the current page and crawl these URLs and send the response to our 2nd function parse_tweet ()
def find_tweets(self, response):
tweets = response.xpath('//table[@class="tweet "]/@href').getall()
logging.info(f'{len(tweets)} tweets found')
for tweet_id in tweets:
tweet_id = re.findall("\d+", tweet_id)[-1]
tweet_url = 'https://twitter.com/anyuser/status/' + \
str(tweet_id)
yield scrapy.Request(tweet_url, callback=self.parse_tweet)
# finding and visiting next page
next_page = response.xpath(
'//*[@class="w-button-more"]/a/@href').get(default='')
logging.info('Next page found:')
if next_page != '':
next_page = 'https://mobile.twitter.com' + next_page
yield scrapy.Request(next_page, callback=self.find_tweets)
Now we will find the next URL for Load older Tweets button and crawl it and send the response to our current find_tweets() function. This way our crawler will keep clicking on the Load older Tweet button recursively if it is available on every crawl. This means we will visit all the results pages one by one.
Finding all the data from an individual tweet — parse_tweet( ) function
def parse_tweet(self, response):
logging.info('Processing --> ' + response.url)
username = response.xpath(
'//*[@class="permalink-inner permalink-tweet-container"]//*[@class="username u-dir u-textTruncate"]/b/text()').get(
default='')
full_name = response.xpath(
'//*[@class="permalink-inner permalink-tweet-container"]//*[@class="FullNameGroup"]/strong/text()').get(
default='')
tweet_text = ' '.join(response.xpath(
'//*[contains(@class,"permalink-inner permalink-tweet-container")]//*[@class="js-tweet-text-container"]/p//text()').getall()).strip()
image_list = response.xpath(
'//*[contains(@class,"permalink-inner permalink-tweet-container")]//*[@class="AdaptiveMediaOuterContainer"]//img/@src').getall()
date_time = response.xpath(
'//*[contains(@class,"permalink-inner permalink-tweet-container")]//*[@class="js-tweet-details-fixer tweet-details-fixer"]/div[@class="client-and-actions"]/span[@class="metadata"]/span/text()').get(
default='')
date_time = parser.parse(date_time.replace('-', '')).strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
retweets = response.xpath(
'//*[contains(@class,"permalink-inner permalink-tweet-container")]//*[@class="js-tweet-details-fixer tweet-details-fixer"]/div[@class="js-tweet-stats-container tweet-stats-container"]//*[@class="js-stat-count js-stat-retweets stat-count"]/a/strong/text()').get(
default='')
likes = response.xpath(
'//*[contains(@class,"permalink-inner permalink-tweet-container")]//*[@class="js-tweet-details-fixer tweet-details-fixer"]/div[@class="js-tweet-stats-container tweet-stats-container"]//*[@class="js-stat-count js-stat-favorites stat-count"]/a/strong/text()').get(
default='')
replies = response.xpath(
'//*[contains(@class,"permalink-inner permalink-tweet-container")]//*[contains(@id,"profile-tweet-action-reply-count")]/parent::span/@data-tweet-stat-count').get(
default='')
mentions = get_mentions(tweet_text)
hashtags = get_hashtags(tweet_text)
cta = get_links(tweet_text)
result = {
'username': username.lower(),
'full_name': full_name,
'twitter_url': response.url,
'tweet_text': tweet_text,
'tweet_time': str(date_time),
'number_of_likes': str(likes),
'no_of_retweets': str(retweets),
'no_of_replies': str(replies),
'mentions': ' | '.join(mentions),
'no_of_mentions': str(len(mentions)),
'hashtags': ' | '.join(hashtags),
'no_of_hashtags': str(len(hashtags)),
'call_to_action': ' | '.join(cta),
'image_url': ' | '.join(image_list),
}
yield result
print(result)
Explanation: Here we will use the current version of twitter (example: https://twitter.com/catsfootprint/status/1213603795663491075) as it turns our it loads all the data even without rendering javascript.
Let's do a sample crawl now.
First of all, lets set up the crawler
Installation
- Download the project(for OS X and Linux)
git clone https://github.com/amitupreti/Hands-on-WebScraping
cd Hands-on-WebScraping/project1_twitter_hashtag_crawler
For Windows users
- Download the project (Windows) here.
- — Extract the project
- — Open cmd and navigate inside the project directory
cd Hands-on-WebScraping/project1_twitter_hashtag_crawler
- Install the dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt --user
- Verify the crawler spider exists
scrapy list
if you see twittercrawler , then you are all set.
Using your hashtags
Open myhashtags.csv file and put your hashtags separated by new line
Crawl and save data in your desired format(JSON,JSON lines,CSV,XML)
For CSV
scrapy crawl twittercrawler -a filename=myhashtags.csv -o mydata.csv
For JSON
scrapy crawl twittercrawler -a filename=myhashtags.csv -o mydata.json
For Jsonlines
scrapy crawl twittercrawler -a filename=myhashtags.csv -o mydata.jl
For XML
scrapy crawl twittercrawler -a filename=myhashtags.csv -o mydata.xml
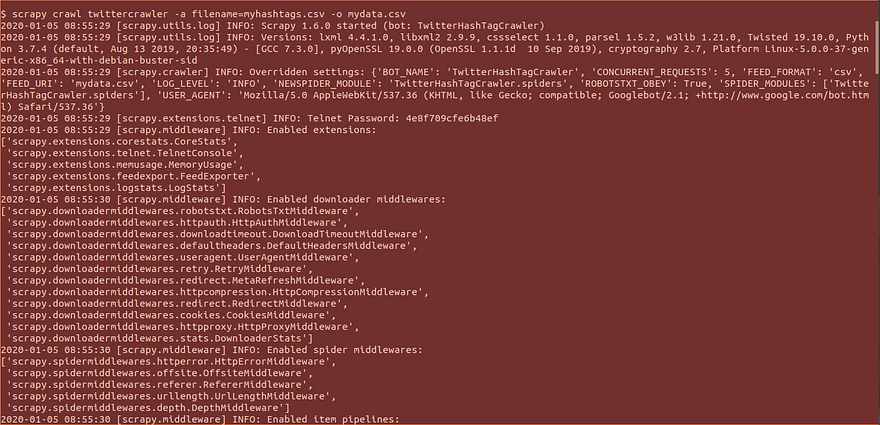
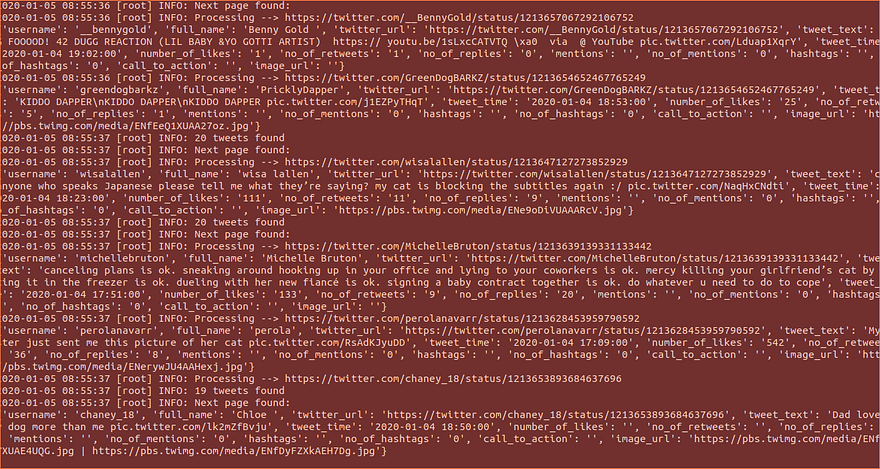
You should now see the data being saved the output file with the format you choose
Speeding up the crawls
If you feel like the crawler is a little slow then find the hashtag.py file in the project and edit the custom settings.
custom_settings = {
'USER_AGENT': 'Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko; compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html) Safari/537.36',
'CONCURRENT_REQUESTS': 2, 'DOWNLOAD_DELAY': 1, 'LOG_LEVEL': 'INFO'}
Here CONCURRENT_REQUESTS is the number of URLs that will be processed parallelly and DOWNLOAD_DELAY is a wait between each request. So, Increase CONCURRENT_REQUESTS and decrease DOWNLOAD_DELAY (minimum value for download delay is 0).
If you have suggestions or find some issues.
Feel free to open an issue or a Pull Request on GitHub.
Thank you for reading.
